A counterbored hole is usually used for when the top of a screw or bolt needs to be flush with, or sit just beneath, the surface of the material it is inserting.
For example, a shoulder screw with a counterbored hole sits flush with the surface, whereas the shoulder screw with a simple clearance hole sits above the surface.
Use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in millimeters.
For example, an ISO M10 shoulder screw with a normal fit counterbored hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 14.5 mm, a counterbore diameter of 23 mm, and a counterbore depth of 9 mm.
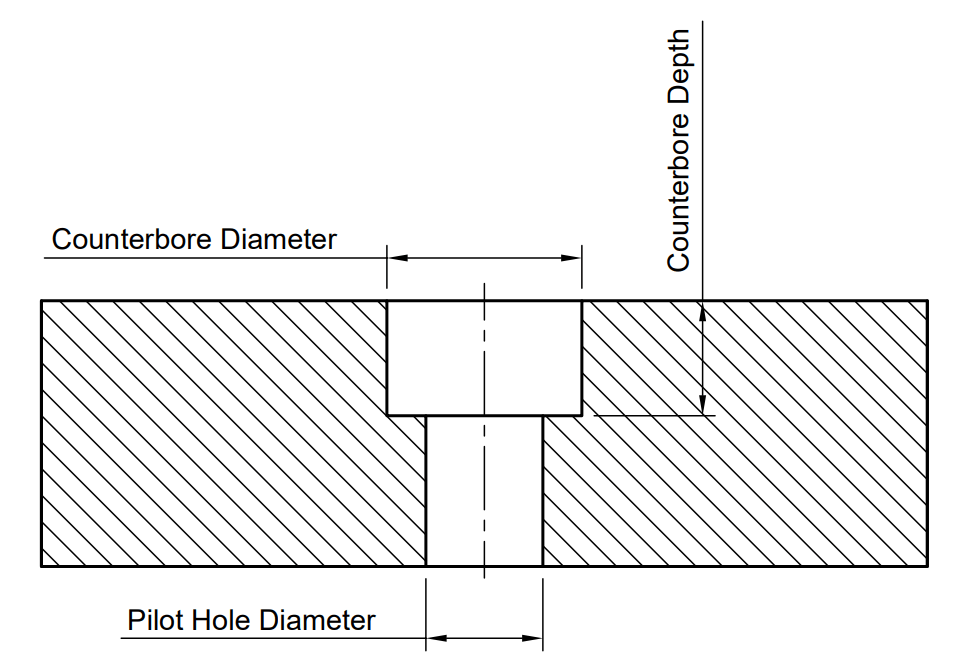
Counterbore Hole Size Chart for Shoulder Screw Fasteners (ISO)
All dimensions are in millimeters.
| Fastener Size (Thread) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Close Fit H12) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Normal Fit H13) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Loose Fit H14) | Counterbore Diameter | Counterbore Depth |
| M5 | 7 | 7.4 | 8 | 13 | 4.5 |
| M6 | 8.4 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 5.5 |
| M8 | 10.5 | 11 | 12 | 19 | 7 |
| M10 | 14 | 14.5 | 15 | 23 | 9 |
| M12 | 17 | 17.5 | 18 | 27 | 11 |
| M16 | 21 | 22 | 24 | 35 | 14 |
| M20 | 27 | 29 | 31 | 42 | 16 |
